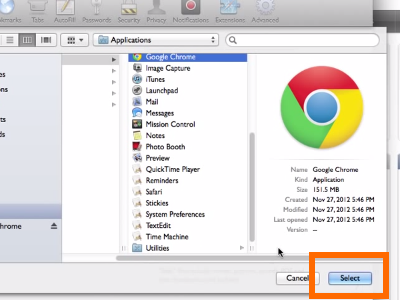
Location Of Applications Google Chrome.app Contents Versions Mac
Flash Player is integrated with Google Chrome as Pepper plug-in. Sometimes, it's necessary for developers to install the Content Debugger to debug their code. These instructions outline how to install and enable the Content Debugger.
Note:
If you have issues with integrated Flash Player plug-in in Chrome, report the issue to Google.
Go to https://www.adobe.com/support/flashplayer/debug_downloads.html and download the Content Debugger installer for the OS in use (Mac OS or Windows).
If installing the Content Debugger for Mac OS, note the version number.
Proceed with installing Flash Player Content Debugger.
Jan 23, 2017 Google embeds Flash Player in Chrome and updates are released by Google. Google recently changed their Flash Player install/update behaviour. When installing Chrome for the first time, Google delays the installation of Flash Player for a few minutes, or until Flash content is viewed, whichever comes first. What Mac OS version do you have?
At the prompt, type the launch command in the following syntax:
<path to chrome app> --ppapi-flash-path=<path to PPAPI plugin> --ppapi-flash-version=<PPAPI Version Installed>
For example:
/Applications/Google Chrome.app/Contents/MacOS/Google Chrome --ppapi-flash-path=/Library/Internet Plug-Ins/PepperFlashPlayer/PepperFlashPlayer.plugin --ppapi-flash-version=19.0.0.185
To confirm that Chrome is using the Content Debugger, navigate to http://helpx.adobe.com/flash-player.html.
Transfer app mac to mac. The results indicate that the debug version is in use:
Your system information Your Flash Version 19.0.0.185 (debug version) Your browser name Google Chrome (PPAPI) Your Operating System (OS) Macintosh (OSX)
In the address field, type the following and press enter: chrome://plugins
Click Details and scroll down to the Flash section.
Disable the integrated Pepper version by clicking Disable. The Location of the integrated version is in the Programs Files directory path.
To confirm Chrome is using the Content Debugger, launch Chrome and navigate to http://helpx.adobe.com/flash-player.html.
The results indicate that the debug version is in use:
Your system information Your Flash Version 19.0.0.185 (debug version) Your browser name Google Chrome (PPAPI) Your Operating System (OS) Windows (Windows 7)
Contents
- Before you begin
- Using a preferences file
- Using the Windows registry
- Updating and uninstalling
- FAQ
- API reference
For information on how to use experimental APIs, see the chrome.experimental.* APIs page.
Usually, users install their own extensions.But sometimes you might want an extensionto be installed automatically.Here are two typical cases:
- An extension is associated with some other software, and the extension should be installed whenever the user installs that other software. The extension could also be uninstalled when the user removes that other software.
- A network admin wants to install the same extensions throughout the company.
An extension that's installed automatically is known as anexternal extension.Google Chrome supports two ways ofinstalling external extensions:
- Using a preferences JSON file
- Using the Windows registry (Windows only)
Both ways support installing an extension from a .crx extensionfile on the user's computer. The preferences JSON file also supports installingan extension hosted at anupdate URL.See hosting for details on hosting an extension.
Before you begin
First, package a.crx fileand make sure that it installs successfully.
If you wish to install from an update URL, ensure that the extensionis properly hosted.
Then, before you edit the preferences file or the registry,make a note of the following:
- The intended location of the extension's
.crxfile, or the update URL from which it is served - The extension's version (from the manifest file or the chrome://extensions page)
- The extension's ID (from the chrome://extensions page when you've loaded the packed extension)
The following examples assume the version is 1.0and the ID is aaaaaaaaaabbbbbbbbbbcccccccccc.
Using a preferences file
Windows note:Until bug 41902 is fixed,you might want to use the Windows registryinstead of the preferences file.
- If you are installing from a file, make the
.crxextensionfile available to the machine you want to install the extension on.(Copy it to a local directory or to a network share for example,servershareextension.crxor/home/share/extension.crx.) - Locate the
external_extensions.jsonfile. If the file doesn't exist, create it. The location depends on the operating system.- Windows:
chrome_rootApplicationchrome_versionExtensions
Example:c:UsersMeAppDataLocalGoogleChromeApplication6.0.422.0Extensions- Mac OS X:
- For a specific user:
~USERNAME/Library/Application Support/Google/Chrome/External Extensions/
For all users:/Library/Application Support/Google/Chrome/External Extensions/The external extensions file for all users is read only if every directory in the path is owned by the user
root, has the groupadminorwheel, and is not world writable. The path must also be free of symbolic links. These restrictions prevent an unprivileged user from causing extensions to be installed for all users. See troubleshooting for details.Note: The above path for all users was added in Chrome 16. Prior versions used a different path, which is now deprecated:
/Applications/Google Chrome.app/Contents/Extensions/. - Linux:
/opt/google/chrome/extensions/
Note: Usechmodif necessary to make sure thatextensions/external_extensions.jsonis world-readable.
- Add an entry to
external_extensions.jsonfor your extension's ID. If you are installing from a file, specify theextension's location and version with fields named 'external_crx' and'external_version'.Example:Note:You need to escapeeach
character in the location.For example,servershareextension.crxwould be'servershareextension.crx'.If you are installing from an update URL, specify the extension's update URLwith field name 'external_update_url'.
Example:If you would like to install extension only for some browser locales,you can list supported locales in field name 'supported_locale'. Locale mayspecify parent locale like 'en', in this case the extension will beinstalled for all English locales like 'en-US', 'en-GB', etc.If another browser locale is selected that is not supported by the extension,the external extensions will be uninstalled. If 'supported_locales' listis missing, the extension will be installed for any locale.
Example: - Save the JSON file.
- Launch Google Chrome and go to chrome://extensions;you should see the extension listed.
Troubleshooting Mac OS permissions problems
On Mac OS, the external extensions file for all users is only read if file system permissions prevent unprivelaged users from changing it. If you do not see external extensions installed when Chrome is launched, there may be a permissions problem with the external extensions preferences file. To see if this is the problem, follow these steps:
- Launch the Console program. You can find it under /Applications/Utilities/Console.
- If the leftmost icon in the Console says 'Show Log List', click that icon. A second column appears at the left.
- Click 'Console Messages' in the left pane.
- Search for the string Can not read external extensions. If there is a problem reading the external extensions file, you will find an error message. Look for another error message directly above it, which should explain the issue. For example, if you see the following error: 'Path /Library/Application Support/Google/Chrome is owned by the wrong group', you need to use
chgrpor the Finder's Get Info dialog to change the directory's group owner to the Administrator group. - After fixing the issue, relaunch Chrome. Test that the external extension is now installed. It is possible that one permissions error keeps Chrome from detecting a second error. If the external extension was not installed, repeat these steps until you do not see an error in the Console application.
Using the Windows registry
- Make the
.crxextension file availableto the machine you want to install the extension on.(Copy it to a local directory or to a network share —for example,servershareextension.crx.) - Find or create the following key in theregistry:
- 32-bit Windows:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESoftwareGoogleChromeExtensions - 64-bit Windows:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESoftwareWow6432NodeGoogleChromeExtensions
- 32-bit Windows:
- Create a new key (folder)under the Extensions key with thesame name as the ID of your extension(for example,
aaaaaaaaaabbbbbbbbbbcccccccccc). - Create two string values (
REG_SZ) named 'path' and 'version', and set them to the extension's location and version. For example:- path:
servershareextension.crx - version:
1.0
- path:
- Launch the browser and go tochrome://extensions; you shouldsee the extension listed.
Updating and uninstalling
Google Chrome scans the metadata entriesin the preferences and registryeach time the browser starts, and makesany necessary changes to the installedexternal extensions.
To update your extension to a new version,update the file, and then update the versionin the preferences or registry.
To uninstall your extension(for example, if your software is uninstalled),remove the metadata from the preferences fileor registry.
FAQ
This section answers common questions about external extensions.
Can I specify a URL as a path to the external extension?
Yes, if you use a preferences JSON file. Theextension must be hosted as explained in hosting.Use the 'external_update_url' property to point to anupdate manifest that has the URL for yourextension.
What are some common mistakes when installing with the preferencesfile?
- Not specifying the same id/version as the one listed in the
.crx external_extensions.jsonis in the wrong location- Syntax error in JSON file (forgetting to separate entries with comma or leaving a trailing comma somewhere)
- Extra curly brackets around the top level dictionary
- JSON file entry points to the wrong path to the
.crx(or path specified but no filename) - Backslashes in UNC path not escaped (for example,
'serversharefile'is wrong; it should be'servershareextension') - Permissions problems on a network share
What are some common mistakes when installing with the registry?
- Not specifying the same id/version as the one listed in the
.crx - Key created in the wrong location in the registry
- Registry entry points to the wrong path to the
.crxfile (or path specified but no filename) - Permissions problems on a network share
What if the user uninstalls the extension?
If the user uninstalls the extension through the UI, it will nolonger be installed or updated on each startup. In other words, theexternal extension is blacklisted.
How do I get off the blacklist?
If the user uninstalls your extension, you should respect thatdecision. However, if you (the developer) accidentally uninstalledyour extension through the UI,you can remove the blacklist tagby installing the extension normallythrough the UI, and then uninstalling it.
API reference: chrome.apiname
Properties
getLastError
Methods
method name
Undocumented.
A description from the json schema def of the function goes here.
Parameters
Returns
Callback function
The callback parameter should specify a function that looks like this:
If you specify the callback parameter, it should specify a function that looks like this:
This function was added in version . If you require this function, the manifest key minimum_chrome_version can ensure that your extension won't be run in an earlier browser version.
Events
event name
Undocumented.
A description from the json schema def of the event goes here.